The plant cell
Cell structures and their functions
Cell Wall
It is a rigid layer which is composed of polysaccharides cellulose, pectin and hemicellulose. It is located outside the cell membrane. It also comprises glycoproteins and polymers such as lignin, cutin, or suberin.
The primary function of the cell wall is to protect and provide structural support to the cell. The plant cell wall is also involved in protecting the cell against mechanical stress and providing form and structure to the cell. It also filters the molecules passing in and out of it.
The formation of the cell wall is guided by microtubules. It consists of three layers, namely, primary, secondary and the middle lamella. The primary cell wall is formed by cellulose laid down by enzymes.
Cell membrane
It is the semi-permeable membrane that is present within the cell wall. It is composed of a thin layer of protein and fat.
The cell membrane plays an important role in regulating the entry and exit of specific substances within the cell.
For instance, cell membrane keeps toxins from entering inside, while nutrients and essential minerals are transported across.
Nucleus
The nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that is present only in eukaryotic cells. The vital function of a nucleus is to store DNA or hereditary information required for cell division, metabolism and growth.
- Nucleolus: It manufactures cells’ protein-producing structures and ribosomes.
- Nucleopore: Nuclear membrane is perforated with holes called nucleopore that allow proteins and nucleic acids to pass through.
Plastids
They are membrane-bound organelles that have their own DNA. They are necessary to store starch and to carry out the process of photosynthesis. It is also used in the synthesis of many molecules, which form the building blocks of the cell. Some of the vital types of plastids and their functions are stated below:
Leucoplasts
They are found in the non-photosynthetic tissue of plants. They are used for the storage of protein, lipid and starch.
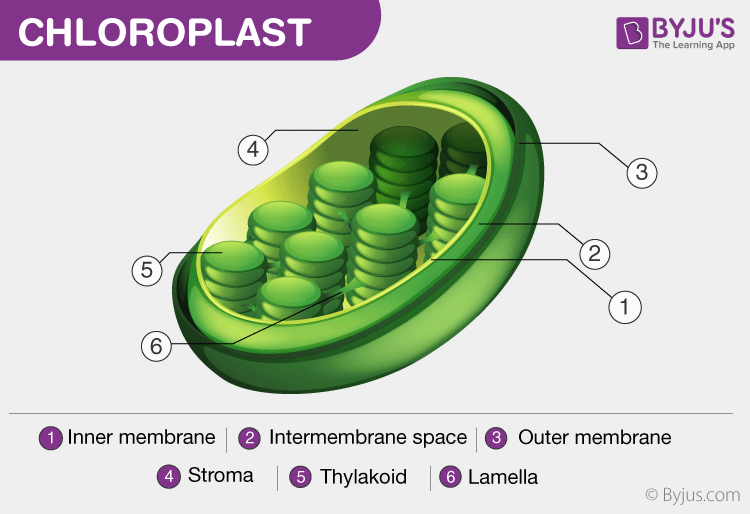
Chloroplasts
It is an elongated organelle enclosed by phospholipid membrane. The chloroplast is shaped like a disc and the stroma is the fluid within the chloroplast that comprises a circular DNA. Each chloroplast contains a green coloured pigment called chlorophyll required for the process of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll absorbs light energy from the sun and uses it to transform carbon dioxide and water into glust.
.png)
.jpg)
Very informative, Thank you.
ReplyDeleteGreat information, thanks
ReplyDeleteForgot about all this when i finished school. Thank you for the education
ReplyDeleteI didn't really get to understand this in school..Thanks very much for helping me understand.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteThanks, I have learned a lot in this blog, keep up the good work
ReplyDeleteThat’s my teacher ! 😇 keep it up bby gal 🫡
ReplyDelete